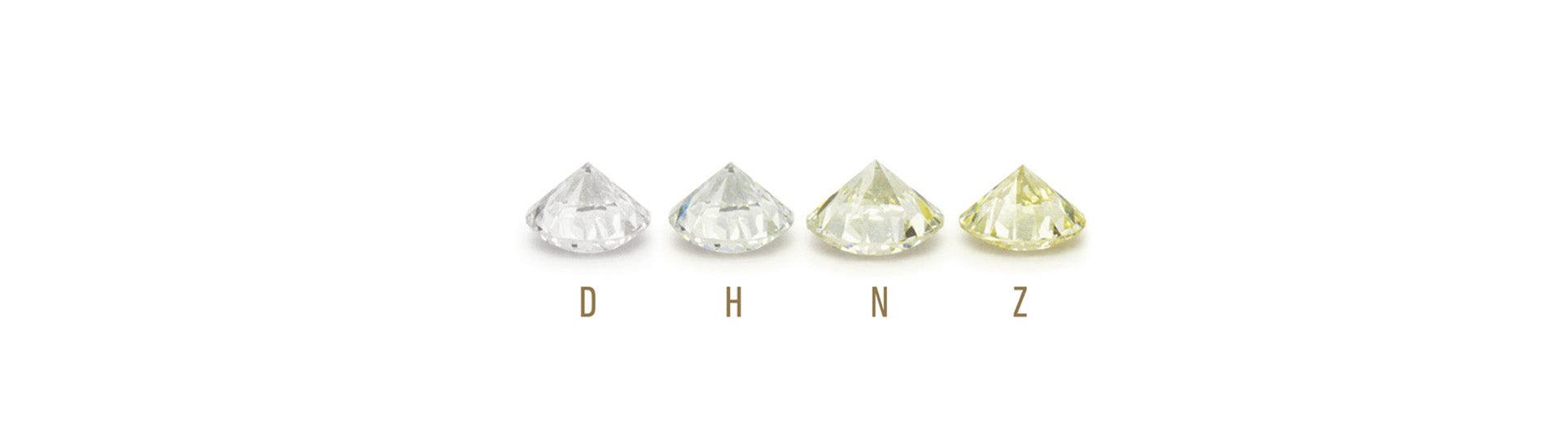
The Colour of Your Diamond

One of the 4Cs on a diamond grading report refers to colour and it's one of the four main characteristics that you will wish to consider when buying your diamond. At Monroe Yorke Diamonds we try to make the distinctions easier to understand before you purchase, and explain why certain colours of diamonds will command higher prices.
Loose diamonds must be graded before they are mounted or put in a setting. This is because surrounding colours can permeate the true colour of the stone. For example a yellow gold setting will make a diamond look less yellow. A white gold or platinum setting will emphasise colour. First and foremost, diamonds are graded by GIA, AGS and HRD thus:~
| D - E - F | Colourless Diamonds (Carried by Monroe Yorke Diamonds) |
| G - H - I - J | Near Colourless (Carried by Monroe Yorke Diamonds) |
| K - L - M | Faintly Tinted, usually yellow (Not carried by Monroe Yorke Diamonds) |
| N - O - P - Q - R | Lightly tinted, usually yellow. Tint can be seen with the naked eye (Not carried by Monroe Yorke Diamonds) |
| S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z | Tinted, usually yellow, may progress to brownish. Tint visible to the naked eye (Not carried by Monroe Yorke) |

- These grades apply to diamonds that are colourless, or those that are yellow through yellowish brown, as in the above diagram. They do not apply to fancy coloured diamonds. Fancy coloured diamonds have separate colour grading standards.
- When referring to colour, a grading report will grade a diamond's lack of colour or whiteness.
- D is the highest colour grade with Z being the lowest.
Fancy Coloured Diamonds
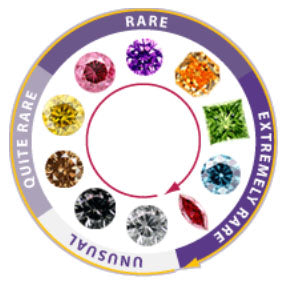
Today, diamond purchasers and collectors are spoilt for choice in the colour spectrum. These unusual diamonds are simply stones that have undergone certain natural processes during their formation deep within the Earth. Beautiful colours are achieved depending on the presence of gases or minerals within the sphere of the stone
They are discovered in myriad hues such as pink, red, green, violet, purple, blue and orange. In comparison to clear or 'white' diamonds, fancy coloured diamonds account for only 0.001% of the 80,000 carats that are mined every year. Formation conditions would have to include or result in:~
- Manganese inclusions within a diamond result in pink and red diamonds
- The presence of nitrogen will result in a yellow diamond
- Exposure to irradiation will result in a green diamond
The deeper the colour of the diamond, the higher the grade. The grading of these stones differs from how other diamonds are graded. Here is some guidance from Monroe Yorke Diamonds about your chosen fancy coloured diamond:~

In the above diagram, you can see how a pink diamond can range in the intensity of it's colour, from 'intense colour' to 'faint colour'.
- The predominant colour will determine how the diamond is named i.e. pink
- Any secondary colour within the stone will result in the diamond being described as '-ish' as with 'purplish pink'. This colour is known as a modifier.
- Where a diamond has a presence of two equal colours, they will both be named, such as 'red~pink'
- The higher the intensity of colour, the higher the value
Diamond Colour Purity
For the traditionalist and collectors who wish to purchase a pure diamond, without perceptible colour, we suggest a colourless diamond in the higher grades of D – E – F. The grades from G~J will be a diamond with superior value and a 'nearly colourless' description

